What Is Digital Marketing?
Digital marketing means using digital channels, like search engines, social media, email, mobile apps, and websites, to promote a product or service. This umbrella term also includes marketing using digital devices such as TV or radio

Examples of online digital marketing include:
- Search engine optimization (SEO): optimizing a website to improve its visibility and ranking on search engines like Google.
- Pay-per-click advertising (PPC): paying for advertisements to appear on search engine results pages or social media platforms.
- Social media marketing: creating and sharing content on social media platforms like Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram to increase brand awareness and engagement.
- Content marketing: creating and sharing valuable content, such as blog posts, e-books, or videos, thus attracting and retaining a specific audience.
- Leveraging traditional offline media for advertising: using radio and TV marketing, billboard advertising, print, and in-person events.
Analysts predict the global digital advertising and marketing sector will reach $786.2 billion by 2026, with clicks and display ads among the most dominant forms.
Then there’s offline digital marketing like:
- Out-of-Home Advertising: This involves using billboards, transit ads, or other types of visual media to promote your brand or product. This can be a great way to reach a broad audience and create a strong visual impression.
- TV Marketing: where you promote your products in the form as adverts, infomercials, or even demonstrations.
- Radio marketing: Trailers and commercials promoting your product to listeners.
In other reports by PR Newswire, digital marketing is worth an estimated $460 billion in the US.
Digital marketing first became popular in the early 2000s, but it’s been around much longer.
Like, WAY longer. About 100 years longer, to be exact.
Here’s a pic of the first digital marketer in history:

His name was Guglielmo Marconi, and he was born in 1874.
In 1896, Marconi became the first human to demonstrate a “public transmission of wireless signals” when he invented the radio.
While it would take another ten years for the radio to reach the general public, it sure didn’t take the creators long to realize they could use it to sell stuff.
The first live broadcast was from an opera performance at the Met, and guess what people did after it?
They bought show tickets!
Digital marketing was born.
Online Digital Marketing Overview
The two main pillars of digital marketing are online and offline. That said, since I’ll talk about online marketing in a separate guide, I’ll only mention the different areas of online marketing here for completeness.
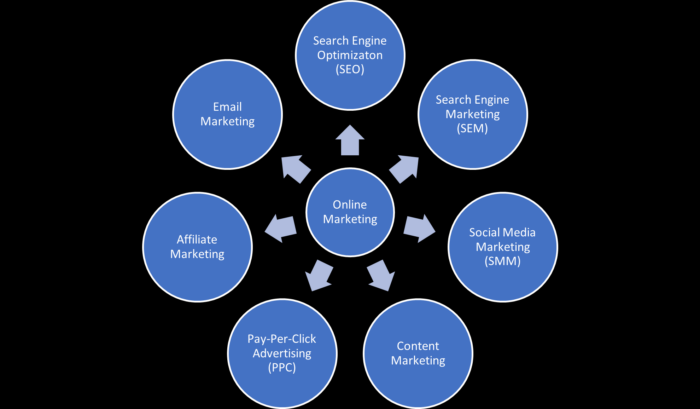
The seven big categories of online marketing are:
- Search engine optimization (SEO)
- Search engine marketing (SEM)
- Content marketing
- Social Media Marketing (SMM)
- Pay-per-click advertising (PPC)
- Affiliate marketing
- Email marketing
Intro to Offline Digital Marketing
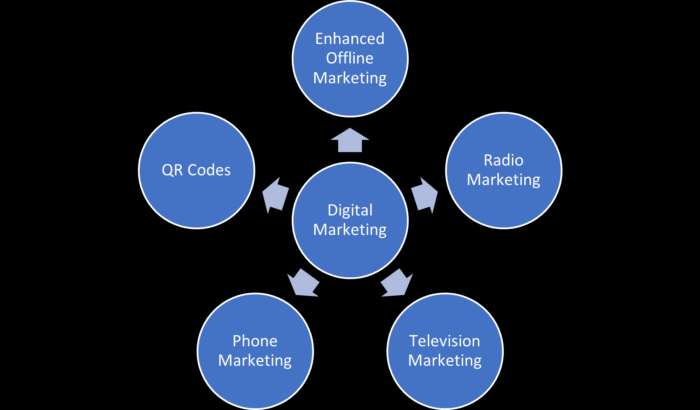
There are five main categories of offline digital marketing:
- Enhanced offline marketing
- Radio marketing
- Television marketing
- Phone marketing
- QR codes
As the name suggests, enhanced offline marketing is performed solely offline. It integrates traditional offline marketing methods like direct mail, TV, radio ads, billboards, or event marketing.
First, let’s look at an example of enhanced offline marketing in action. Let’s say your restaurant uses iPads for your customers to place orders. In that case, the offline experience of eating Thai food is enhanced with this electronic device.
Next, there’s radio marketing. So the next time you hear an annoying, over-enthusiastic car dealer shout every word of their commercial, thank Mr. Marconi.
Of course, we can’t forget television marketing. Although streaming is hugely popular, traditional TV advertising still has its part. Statistics show revenues from TV advertising reached 171 billion in 2022.
Although phone marketing might seem old-fashioned, 102 call centers opened in the United States in 2021, and call centers made an annual revenue of $21.2 million.
Enhanced Offline Marketing
What’s the difference between a billboard in the desert of Arizona and a billboard in New York City’s Times Square?
The size? The product?
Three letters: LED. Light emitting diodes.
All of the billboards in Times Square are electronic!
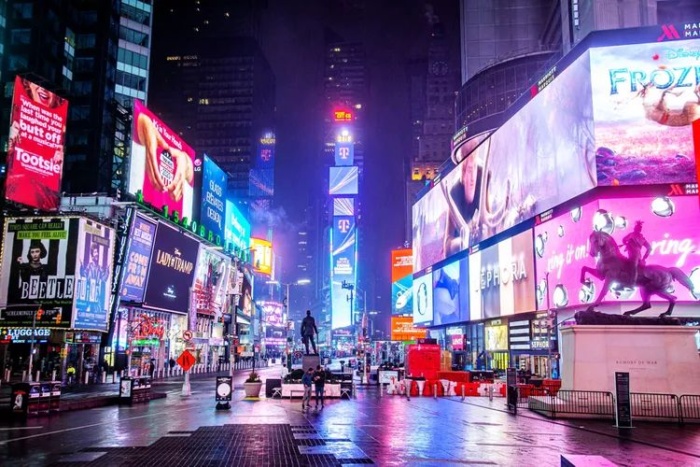

Credit: NICOLAS ECONOMOU / GETTY IMAGES
Why? Because in the desert of Arizona, no one’s competing with you for people’s attention. If you have a billboard at all, you win.
In Times Square, attention is probably more valuable than anywhere else in the world, with more than 360,000 visitors daily.
With a constant flow of buses, taxis, promoters shouting, and electronic billboards, there are distractions everywhere you go. Some of the billboards are even interactive, showing live feeds of the people on the square or pictures of customers.
Here’s another example.
What do you see when you walk into an Apple Store these days?
People leaning over iPads, Macbooks, and iPhones.
Product demos should be an essential part of your digital marketing strategy if you have any type of electronic product.
Another example is those free trial CDs that AOL sent out in the early 90s—you may remember those were everywhere at one point. All those CDs may have been annoying, but they’re likely a big reason for AOL’s early success.
Radio Marketing
The radio isn’t dead. It’s thriving: Just look at the stats:
- 83 percent of Americans listen to radio weekly.
- People spend an average of 99 minutes per day listening to radio content.
- Revenue from radio is predicted to reach 33.53 billion.
For brands, radio can be a smart move for offline digital marketing. These days, hosts read out advertising sponsorships at the beginning of shows when they’re more likely to get listeners’ attention.
If this is an approach you’re considering, find your local radio stations with a quick Google search. Look for a station whose audience reflects your company’s target demographic; radio stations should provide the data that helps you select the right fit.
For example, if your company sells maternity products, search for a radio program whose average listener is a female between 24 and 40.
If you go the traditional radio advertising route, the key is to be entertaining and catch the listener’s attention.
Here are some tips for creating a great advert for traditional radio:
- Keep it brief and memorable: Radio ads are generally short, typically 30 seconds or less, so focus on delivering your message clearly, concisely, and in a memorable way. Use simple language and a clear call to action.
- Focus on your audience: Understand your target audience and tailor your message to their needs and interests. Use language and tone that resonates with them, and highlight the benefits of your product or service.
- Use sound creatively: Since you can’t rely on visuals, use sound to capture the listener’s attention and make an emotional connection. For example, consider using music, sound effects, or voiceovers to create a sense of atmosphere or reinforce your message.
- Repeat your message: Repetition is critical in radio advertising. Repeat your brand name and message multiple times to ensure it sticks in the listener’s memory.








































